Background
Improvements in resource efficiency and waste reduction coupled with new business models are likely to become increasingly important for manufacturing. Recently much attention has been paid to bioeconomy transitions. A bioeconomy, while based on using renewable resources, is not sustainable per se as even renewable resources are limited. This project adopts the concept of a circular bioeconomy – referring to the efficiency in and reuse of bio-based resources, and explores the implications of circular bioeconomy for the renewal of manufacturing. Circular economy refers to closing material and resource loops reducing pressure on virgin natural resources by extending the use time of products, their parts and materials, decreasing the amount of energy use and pollution from the production of new products, and cutting production and post-consumer volumes of waste. Frontrunners can benefit from circular economy by innovative solutions of product design to new resource efficient or frugal business and market models. Additionally, new ways of turning waste, by-products and side-flows into a resource can create new business.
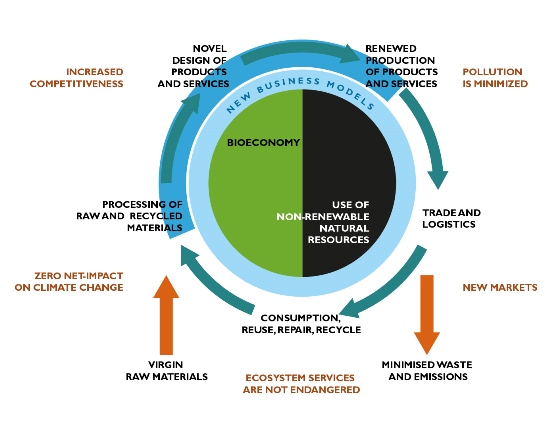
The RECIBI project will assess the potential of circular bioeconomy for the sustainable renewal of manufacturing by a careful analysis of selected frontrunner cases in forest based industries in Finland and in Sweden. In addition, the project will produce new knowledge on how policies can support the renewal of manufacturing and what demands the renewal puts on policies for a sustainable circular economy. Its novel value is in the combination of innovation policy analyses to cross-country comparisons of frontrunner value chains connected to circular bioeconomy and their positive and negative life cycle impacts.
Aims
The aims of the project are
- to better understand the potential of circular economy for sustainable renewal of manufacturing in bio-based industries with particular focus on novel value chains
- to provide novel insights into the role of innovation policies in facilitating the shift towards sustainable, circular bioeconomy in Finland and Sweden, and
- to create policy recommendations based on the new insights and lessons learned internationally.
Research questions:
- What are the similarities and differences in the renewal of manufacturing in Finland and Sweden with respect to innovative bio-based value chains and materials, and how can the sustainability of renewed manufacturing be analysed and documented?
- How can innovative and competitive renewal of manufacturing through novel value chain and business models contribute to the emergence of a circular bioeconomy, and what challenges and opportunities do present and expected circular economy policies create for the renewal of manufacturing?
- How can the regional environmental, economic and social benefits of the renewal be demonstrated or verified on micro and macro-economic scale?
- What challenges does the renewal of manufacturing through circular economy pose for innovation policy and its coherence with other policy domains (e.g. environmental policy, taxation, transport policy) in Finland and Sweden?
- Where should Finnish and Swedish innovation policies - defined broadly as cross-domain policies influencing innovation - focus to effectively contribute to renewal of manufacturing towards circular economy and what lessons can be drawn from the similarities and differences between the two countries and internationally, especially from the Netherlands?
Work packages
WP1 Case study refinement and analytical framework
WP2 Sustainable renewal through novel value chains and business models
WP3 Sustainability performance as innovation competence
WP4 Innovation policy for circular economy oriented renewal
WP5 Synthesis, communication and management
Research Team
SYKE’s Environmental Policy Programme:
Dr. Petrus Kautto, Senior Researcher
Ms. Tiina Jääskeläinen, Researcher
SYKE’s Centre for Sustainable Consumption and Production:
Dr. , Senior Research Scientist, Project leader, WP3 leader
Ms. , Senior Research Scientist
Mr. Jachym Judl, Researcher
Prof. Ilmo Mäenpää
SYKE’s Climate Change Programme:
Prof. Mikael Hildén, Director, WP4 co-leader
International Institute for Industrial Environmental Economics, University of Lund, Sweden:
Dr. Åke Thidell, Senior Researcher, Lecturer, WP2 co-leader (iiiee.lu.se)
Dr. Carl Dalhammar, Assistant Professor, WP4 co-leader (iiiee.lu.se)
Dr. Håkan Rodhe, Associate Professor (iiiee.lu.se)
Dr. Philip Peck, Associate Professor (iiiee.lu.se)
Aalto University, School of Business, Helsinki:
Dr. Armi Temmes, Professor of Practice, WP2 co-leader (aalto.fi)
Dr. Mika Kuisma, Senior Researcher (aalto.fi)
Further information
Senior Research Scientist Riina Antikainen, Finnish Environment Institute (SYKE) fistname.surname@ymparisto.fi