Shortcut: http://www.syke.fi/projects/epic
Project description
Residues of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) enter the environment mainly as a result of consumption of pharmaceutical products (excretion) and via unused pharmaceutical waste or via emissions from pharmaceutical manufacturing plants. The complex behavior and impact of APIs in the environment is not yet well known, but there is indication of harmful effects of some groups of APIs (e.g. endocrine disrupting hormones, behavioral changes in organisms and antimicrobial resistance enhancing antibiotics) to ecosystems and some APIs are known to be extremely persistent and bioaccumulative.
The challenges related to the presence of pharmaceuticals in environment and wastewater as well as in urea and in sewage sludge and for its exploitation have been recognized, despite their high nutrient content. Being a significant technical, economic and health issue, it is necessary to identify how the pharmaceutical residue in the environment and consequently food production can be most effectively minimized.
API load into the environment can be reduced by introducing advanced treatment technologies at municipal waste water treatment plants (WWTPs) or at primary emission sources. Removing API residues at primary source is technically more efficient than removal from MWWP effluents, sewage sludge, or drinking water.
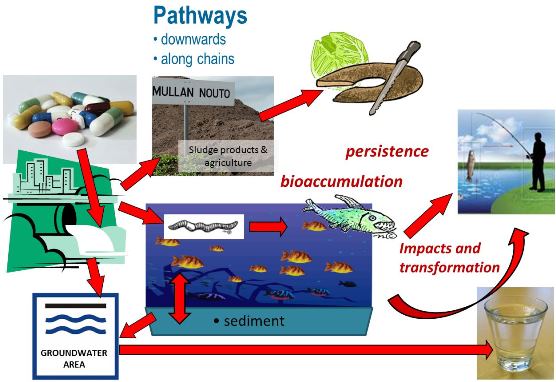
Figure 1. Runaway Pharmaceuticals?
Objectives
This project aimed to identify the APIs entering the waste water stream at different sources and testing effective technological solutions to treat APIs at their primary emission sources. The different technologies were tested in pilot studies. In support of new technologies, the project sought pollution prevention instruments in collaboration with key stakeholders.
Work packages
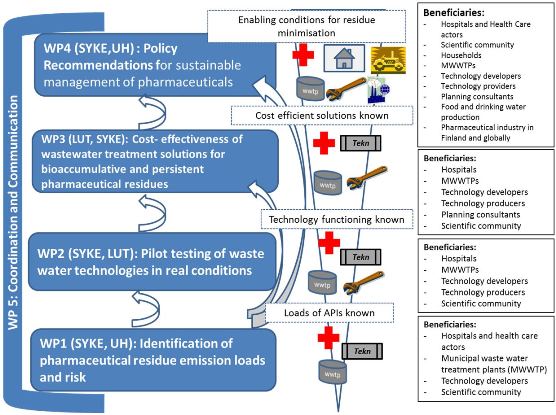
Figure 2. Research Organizations in charge of Work Packages (WP), Value Network and Contribution of WPs.
Project organization

Figure 3. Partners in EPIC consortium.
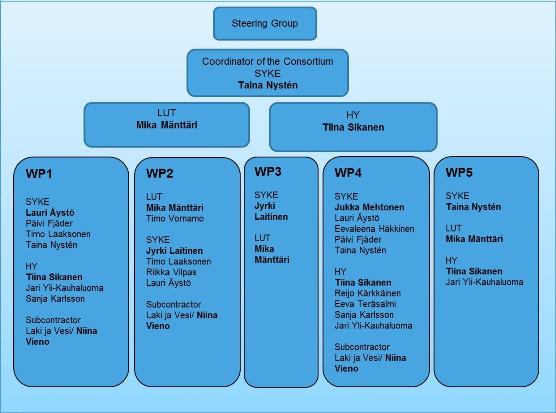
Figure 4. Structure of the project organization. The researchers in charge are written in bold font.
Research partners and Coordinators
The Consortium of Project and SYKE: PhD, Leading Expert Taina Nystén
LUT: Professor Mika Mänttäri
HY: Title of Docent Tiina Sikanen
Subcontractor Law and Water: D.Sc. (Tech.), Water Expert Niina Vieno
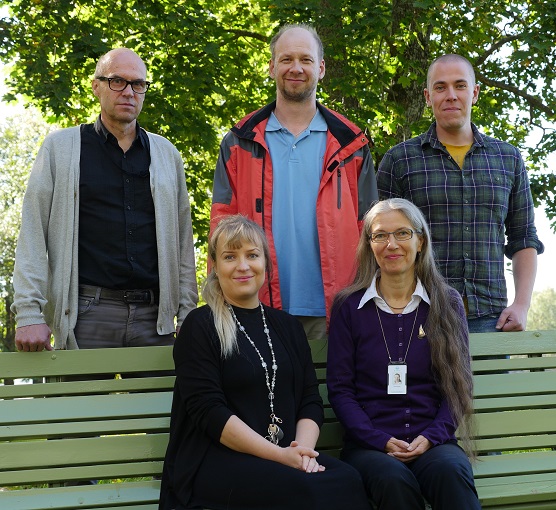

Coordinators of SYKE: Standing from left to right Jyrki Laitinen (WP3), Jukka Mehtonen (WP4) & Lauri Äystö (WP1) and sitting from left to right Päivi Fjäder & Taina Nystén (project consortium, SYKE & WP5) © Kari Kallio

Mika Mänttäri (LUT)
|

Tiina Sikanen (HY)
|
Investigations at the test site

A composite sample being bottled from the sampling container. © Lauri Äystö
|

Samples of influent waste water ready for shipping. © Lauri Äystö
|
Samples being packed with cool packs for shipping. © Lauri Äystö
|

Dewatered sewage sludge being stirred to produce a representative composite sample. © Lauri Äystö
|

Sludge sample being canned for shipping © Lauri Äystö
|

Equipment for PCD oxidation (Pulsed Corona Discharge) © Timo Vornamo
|
Key results
Final report
EPIC_Content-Stakeholders-Benefits-Further information
EPIC_WP1-Emissions and risk identification
EPIC_WP2-Development of new Cleantech solutions
EPIC_WP3-Cost-effectiveness of waste water treatment solutions at different sources
EPIC_WP4-Policy recommendations for sustainable management for pharmaceuticals
Events
17.5.2019 Final seminar of the EPIC project
Nystén T. Policy brief Environmental drug load can be reduced & Efficient Treatment of Pharmaceutical Residue at Source – EPIC
Äystö L. Pharmaceutical load from primary emission sources to WWTPs and from WWTPs into the environment
Sikanen T. Biotransformation of drugs
Mänttäri M. How to get rid of pharmaceutical residue
Laitinen J. Cost-effectiveness of waste water treatment solutions at different sources
Mehtonen J. Pharmaceuticals in environmental permits
Teräsalmi E. Including environmental criteria for drug regulation
Karlsson S. Environmental classification of pharmaceuticals - Implementation to Finland
Vieno N. Conclusions of the EPIC 17.5.2019 seminar
6.9.2018 Techniques for removing pharmaceuticals from water
Mänttäri M. Evaluation of technologies for the removal of pharmaceuticals from wastewaters
Ek M. Advanced enzymatic degradation
More information
- The Consortium of Project and WP5: FT, Leading Expert Taina Nystén, (Syke) firstname.lastname@syke.fi
- WP1: M.Sc. (environmental science), Lauri Äystö & M.Sc. in Agriculture and Forestry (Limnology), Researcher Päivi Fjäder (Syke), firstname.lastname@syke.fi
- WP2: Professori Mika Mänttäri (LUT), firstname.lastname@lut.fi
- WP3: M.Sc.(Tech), LicEcon, Leading expert Jyrki Laitinen (Syke)
- WP4: M.Sc. in Agriculture and Forestry (Limnology), Senior Coordinator, Jukka Mehtonen (Syke), firstname.lastname@syke.fi