5.2.1 Layout and siting of stations
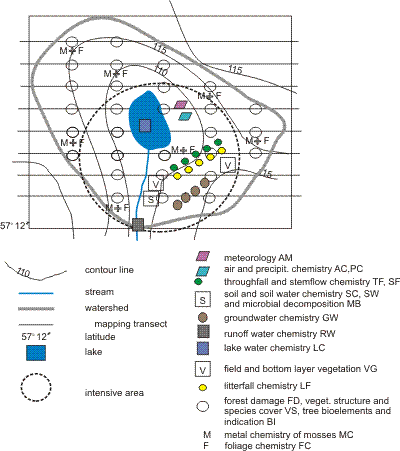
The type of permanent stations used for collecting monitoring data for different subprogrammes of the IM programme varies considerably (plots, groups of trees, sampling sites etc.). The location of stations depends on the heterogeneity of soil, forest stands and vegetation. The plots used for site representative monitoring are located throughout the monitoring site (see circular plots in Figures 5.5 and 5.7). The other stations are preferably located in the main habitat type or types of the monitoring site ( Figure 5.7).
At least two stations for each subprogramme should be established so that the variation of parameters within the monitoring site can be assessed. The stations belonging to different subprogrammes should be grouped to form an intensive area to allow for comparability of monitoring data.
For some subprogrammes (e.g. throughfall and litterfall) the sampling could be done on two scales: 1) in association with the intensive monitoring area (target population = area), 2) transect across catchment (target population = catchment) to relate to catchment deposition. ( Figure 5.7). Transect sampling has not been recommended by ICP Forests and depends on the available resources.
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 5.7 An example of the allocation of monitoring stations at a site with one intensive area. Bedrock/soil material/soil types/tree stands and plant communities, which have been mapped, are also indicated.
|
5.2.2 Intensive area
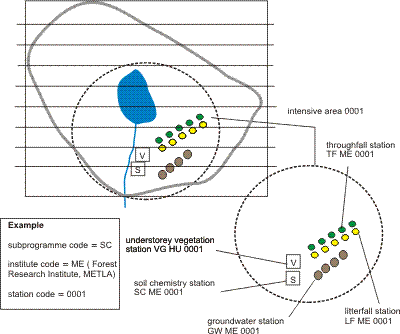
The most common or otherwise typical habitat type or types of the IM site, e.g. vegetation, soil type etc. is/are normally chosen for the stations. The places for different subprogrammes should be located close to one another to allow for wider ecosystem monitoring of a particular habitat. A group of these plots is called an intensive area and the station codes for each subprogramme belonging to the group should be the same (Figure 5.8). The size of an intensive area should not exceed two hectares.
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 5.8 An example of intensive areas and coding of a group of plots. The same 4-digit station code is used for different subprogrammes when the stations are situated on the same intensive area or close to one another on the same habitat type.
|
For maximum added-value and cost-efficiency, all subprogrammes which are not representing the whole site, e. g. metreorology, precipitation chemistry, throughfall, litterfall, field and bottom layer vegetation and soil water should be located in or as near the intensive area/s as possible ( Figure 5.7, 5.8).
5.2.3 Auxiliary stations
Auxiliary stations are stations which can not for some reason be located within the IM site. Stations for subprogrammes meteorology and air chemistry are often located outside the monitoring site due to technical requirements and the cost of the equipment. Auxiliary stations should, however, be avoided because the data are not necessarily representative for the IM site.